Internet, a system architecture that has revolutionized communications and methods of commerce by allowing various computer networks around the world to interconnect. Sometimes referred to as a “network of networks,” the Internet emerged in the United States in the 1970s but did not become visible to the general public until the early 1990s. By 2020, approximately 4.5 billion people, or more than half of the world’s population, were estimated to have access to the Internet.

The Internet provides a capability so powerful and general that it can be used for almost any purpose that depends on information, and it is accessible by every individual who connects to one of its constituent networks. It supports human communication via social media, electronic mail (e-mail), “chat rooms,” newsgroups, and audio and video transmission and allows people to work collaboratively at many different locations. It supports access to digital information by many applications, including the World Wide Web. The Internet has proved to be a spawning ground for a large and growing number of “e-businesses” (including subsidiaries of traditional “brick-and-mortar” companies) that carry out most of their sales and services over the Internet. (See electronic commerce.)
Origin And Development
Early networks
The first computer networks were dedicated special-purpose systems such as SABRE (an airline reservation system) and AUTODIN I (a defense command-and- control system), both designed and implemented in the late 1950s and early 1960s. By the early 1960s computer manufacturers had begun to use semiconductor technology in commercial products, and both conventional batch-processing and time-sharing systems were in place in many large, technologically advanced companies. Time-sharing systems allowed a computer’s resources to be shared in rapid succession with multiple users, cycling through the queue of users so quickly that the computer appeared dedicated to each user’s tasks despite the existence of many others accessing the system “simultaneously.” This led to the notion of sharing computer resources (called host computers or simply hosts) over an entire network. Host-to-host interactions were envisioned, along with access to specialized resources (such as supercomputers and mass storage systems) and interactive access by remote users to the computational powers of time-sharing systems located elsewhere. These ideas were first realized in ARPANET, which established the first host-to-host network connection on October 29, 1969. It was created by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. Department of Defense. ARPANET was one of the first general-purpose computer networks. It connected time-sharing computers at government-supported research sites, principally universities in the United States, and it soon became a critical piece of infrastructure for the computer science research community in the United States. Tools and applications—such as the simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP, commonly referred to as e-mail), for sending short messages, and the file transfer protocol (FTP), for longer transmissions—quickly emerged. In order to achieve cost- effective interactive communications between computers, which typically communicate in short bursts of data, ARPANET employed the new technology of packet switching. Packet switching takes large messages (or chunks of computer data) and breaks them into smaller, manageable pieces (known as packets) that can travel independently over any available circuit to the target destination, where the pieces are reassembled. Thus, unlike traditional voice communications, packet switching does not require a single dedicated circuit between each pair of users.
Commercial packet networks were introduced in the 1970s, but these were designed principally to provide efficient access to remote computers by dedicated terminals. Briefly, they replaced long-distance modem connections by less- expensive “virtual” circuits over packet networks. In the United States, Telenet and Tymnet were two such packet networks. Neither supported host-to-host communications; in the 1970s this was still the province of the research networks, and it would remain so for many years.
The Internet has become an imperative innovation, without which life has gotten unbelievable. The organization of the Internet stretches out even to the space. Today, we have numerous Internet specialist organizations who encourage us with fast Internet for our homes and workplaces.
Fiber Internet in SHANTIPURI
In any case, have you thought about how does the Internet work? What makes the Internet work? Web is a medium that associates various PCs through and through and ensures that the association is unceasing. At the point when at least two PCs need to convey, they should be associated through wires or a remote association.
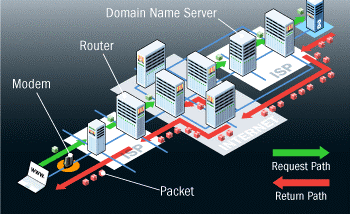
To make the Internet work, certain parts are considered as key segments. The segments can be partitioned into two fundamental parts, the main significant part is the Hardware.
Segments of Internet The equipment incorporates links that convey data from your PC to another. With time, new equipment parts have arisen like the switches, workers, cell towers, satellites, radio’s, cell phones and different gadgets. Every one of these segments structure the organization of organizations. A portion of the components referenced above are viewed as static and others to be fringe. The static ones form the foundation of the Internet. The PC, cell phones other Internet-associated gadgets are usually known as Clients. The data that we traverse the Internet are put away in machines, these machines are called Servers. Hubs are the interfacing focuses along a traffic course. On account of links and fiber optics, actual transmission lines are significant segments that permit those limitless Internet plans and broadband arrangements to arrive at your home or work environment. The transmission lines can likewise be remote signs from satellites, phone or 4G pinnacles and radio’s.
Fiber Internet in SHANTIPURI
The equipment, notwithstanding, can’t make an organization without the second significant segment of the Internet which are supposed to be the Protocols. A bunch of rules followed by a machine to finish any undertaking is supposed to be a Protocol. On the off chance that there are no basic arrangements of conventions between the machines associated with the Internet, at that point network between these gadgets or machines isn’t possible.The convention should encourage a typical language and a technique for machines to trade data among themselves.
What are the main conventions? What do they do? There are a few conventions that you can think about on the Internet. However, the two most significant conventions in conversations will consistently be the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP).
In straightforward words, these conventions set a few standards with respect to how the data should go through the Internet. Different gadgets should likewise comprehend the language of a specific gadget letting out some data. Without this convention, an immediate association is the solitary choice to communicate data.
Every gadget that is associated with the Internet has an IP address. These IP addresses follow the Internet Protocol, making it simpler to discover another machine through this huge organization. The TCP and the IP conventions make the transmission conceivable when you make an impression on another PC or recover data from it. While communicating something specific, your solicitation first hits the DNS ( Domain Name Servers) looking for the objective worker. It is the dependability of the DNS to point the message the correct way. When the objective gets the message, it can send back a reaction back to your PC.
Fiber Internet in SHANTIPURI
The cycle of the information move must be truly adaptable. This is the reason the Internet is viewed as perhaps the most integral assets today. In the event that you are paying special mind to the best Internet plans for your home or office, we at SAW ENTERPRISES can assist you with best broadband arrangements and rapid Internet. Interface with us now! 9528971710